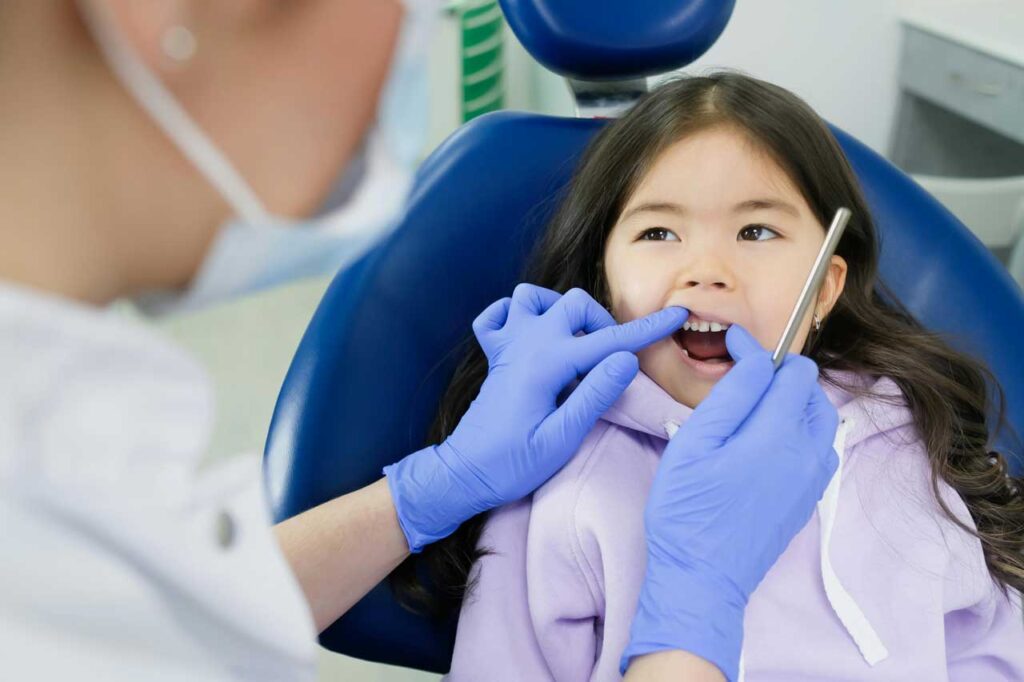
Taking care of your child’s teeth is crucial for their overall health and development. Pediatric dentistry focuses on the dental care of children, from infancy through adolescence, ensuring healthy teeth and gums that will last a lifetime. As a parent, understanding how to care for your child’s teeth, when to begin dental visits, and how to prevent oral issues is essential.
In this blog, we will guide you through pediatric dentistry, from teething to maintaining proper oral hygiene, and provide practical tips for ensuring that your child’s teeth remain strong and healthy.
Need expert pediatric dental care? Visit 32 Dental Care for professional guidance and services tailored to your child’s needs.
When Should Your Child First See the Dentist?
It’s recommended that children see a pediatric dentist by their first birthday, or within six months after the first tooth appears, whichever comes first. Early dental visits help establish a foundation for good oral health and allow the dentist to check for potential problems such as tooth decay, thumb sucking, or misalignment.
The Benefits of Early Dental Visits:
- Early Detection: Issues such as cavities, gum problems, and bite alignment can be identified early.
- Preventive Care: Regular checkups help prevent serious dental issues in the future.
- Good Oral Habits: Children will be introduced to the concept of dental hygiene, making them more likely to adopt healthy habits.
Teething and Infant Oral Care
Teething is the process through which a baby’s first teeth emerge through the gums, typically beginning around six months of age. While teething can be uncomfortable for both the baby and parents, it’s essential to care for the infant’s gums and emerging teeth properly.
Tips for Infant Oral Care:
- Clean the Gums: Even before teeth appear, gently wipe your baby’s gums with a soft, damp cloth after feedings.
- Teething Relief: Offer a chilled teething ring to soothe sore gums. Avoid teething gels that contain benzocaine, as they may not be safe for young children.
- Avoid Sugar: Do not dip pacifiers or bottles in sugary substances, as this can lead to tooth decay once teeth emerge.
Baby Teeth and Their Importance
Baby teeth, also known as primary or deciduous teeth, are crucial for a child’s development, even though they are eventually replaced by permanent teeth. These early teeth help with proper speech development, chewing, and the alignment of future permanent teeth.
Caring for Baby Teeth:
- Brush Early and Often: As soon as the first tooth appears, begin brushing with a soft-bristled toothbrush and a tiny amount of fluoride toothpaste (about the size of a grain of rice).
- Establish a Routine: Brush your child’s teeth twice a day—once in the morning and once before bed—to establish a consistent routine.
- Flossing: Once two teeth begin to touch, start flossing to prevent food particles from getting stuck and to avoid cavities between teeth.
How to Encourage Healthy Habits in Your Child
Children learn best through consistency and positive reinforcement. Establishing good oral hygiene habits early can lead to a lifetime of healthy teeth.
- Make Brushing Fun
-
- Use fun, colorful toothbrushes and toothpaste with your child’s favorite character to make brushing exciting.
- Let them pick their own toothbrush, as this increases their engagement.
- Play music or make up a brushing song to help them stay entertained for the recommended two minutes.
- Be a Role Model
-
- Children are more likely to adopt habits they see their parents doing. Brush your teeth alongside your child to demonstrate the importance of oral hygiene.
- Positive Reinforcement
-
- Praise your child after brushing and flossing, or use a sticker chart to reward consistent efforts.
Preventing Tooth Decay in Children
Tooth decay is one of the most common chronic conditions in children, but it is also preventable with the right care. Pediatric dentists focus on preventing cavities and other dental issues by educating parents and children about the importance of oral hygiene and dietary choices.
Key Factors That Contribute to Tooth Decay:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to build up and cause cavities.
- Dietary Choices: Sugary snacks, juices, and sodas contribute to the development of cavities.
- Frequent Snacking: Constant snacking, especially sugary snacks, can increase the risk of tooth decay.
How to Prevent Tooth Decay:
- Limit Sugary Foods and Drinks: Offer healthy snacks like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Avoid sugary snacks, soda, and juice.
- Brush and Floss Regularly: Make sure your child brushes twice a day and flosses once a day.
- Fluoride Use: Fluoride strengthens enamel and helps prevent cavities. Ask your pediatric dentist if fluoride treatments are right for your child.
- Sealants: Dental sealants are thin protective coatings applied to the chewing surfaces of back teeth, preventing cavities.
Braces and Orthodontic Care for Children
As your child grows, it’s essential to monitor their dental development for signs of misalignment or bite issues. Many children will need orthodontic treatment to straighten their teeth and ensure proper bite function.
When Should Children See an Orthodontist?
- It’s generally recommended that children visit an orthodontist around age 7. At this age, their teeth and jaws are still developing, and early intervention can help guide their dental growth.
Signs Your Child May Need Braces:
- Overbite, underbite, or crossbite
- Crowded or crooked teeth
- Difficulty chewing or biting
Common Pediatric Dental Problems and How to Address Them
Thumb Sucking and Pacifier Use
- Prolonged thumb sucking or pacifier use can affect the alignment of your child’s teeth. If your child continues these habits past age 3, consult with your dentist for advice on how to stop.
Early Loss of Baby Teeth
- Baby teeth usually fall out between the ages of 6 and 12. If your child loses a baby tooth prematurely due to injury or decay, consult your dentist to ensure there’s no impact on the development of permanent teeth.
Cavities in Baby Teeth
- Cavities can develop in baby teeth if not properly cared for. It’s essential to get fillings in cavities to prevent infections and complications, even though the teeth will eventually fall out.
Dental Visits: What to Expect
A typical pediatric dental visit includes the following steps:
- X-rays: To check for cavities and other dental issues.
- Cleaning: A thorough cleaning to remove plaque and tartar from teeth.
- Examination: The dentist will examine your child’s teeth and gums for any issues and may apply fluoride treatment.
- Education: The dentist will provide advice on proper brushing, flossing, and nutrition.
When to Call the Dentist
In some situations, it’s essential to seek immediate dental care:
- Tooth Pain: Persistent pain can indicate a cavity or an infection.
- Broken or Knocked-Out Teeth: If your child experiences an injury, it’s vital to see a dentist as soon as possible.
- Swollen Gums or Bleeding: If your child’s gums are swollen, bleeding, or appear red and inflamed, it could indicate gum disease or infection.
Contact us immediately if your child is experiencing any dental issues. Visit 32 Dental Care for emergency care.
Conclusion
Pediatric dentistry is vital for ensuring your child’s oral health and development. By starting dental visits early, establishing good oral hygiene habits, and preventing issues like cavities, you can set your child up for a lifetime of healthy smiles.